Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

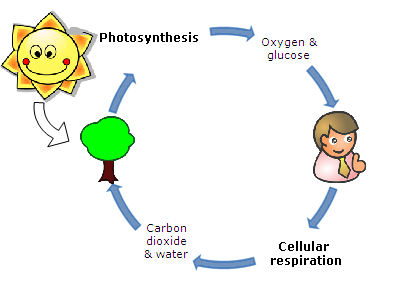
What Is The Purpose Of Cellular Respiration Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Cellular Respiration Definition Equation And Steps Biology Dictionary
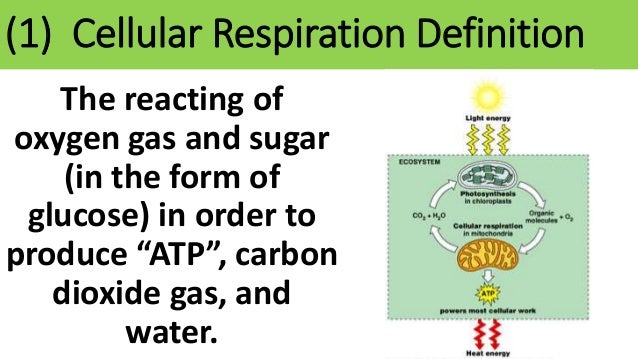
Ths General Biology Unit 1 Our Environment Cellular Respiration Notes

Cellular respiration meaning in biology
Respiration is one of the. Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. Cellular respiration all organisms respire in order to release energy to fuel their living processes. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process while the other two pathways are aerobic. Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell. Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. Biology cellular respiration at a glance. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products. This is the procedure of respiration. Within the eukaryotic cell the process begins in the cytoplasm. Cellular respiration cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate atp. Cellular respiration as the name suggests takes place in individual cells to produce energy for the particular cell. Aerobic respiration is more efficient and can be used in the existence of oxygen while anaerobic respiration doesn t require oxygen. In order to move from glycolysis to the citric acid cycle pyruvate molecules the output of glycolysis must be oxidized in a. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form.
The first step of cellular respiration glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm as the enzymes required for glycolysis are present in the cytoplasm. Cellular respiration definition cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. Cellular respiration is the procedure by which cells obtain their energy in the shape of atp. The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells. How to get a covid antibody test.
Related post:
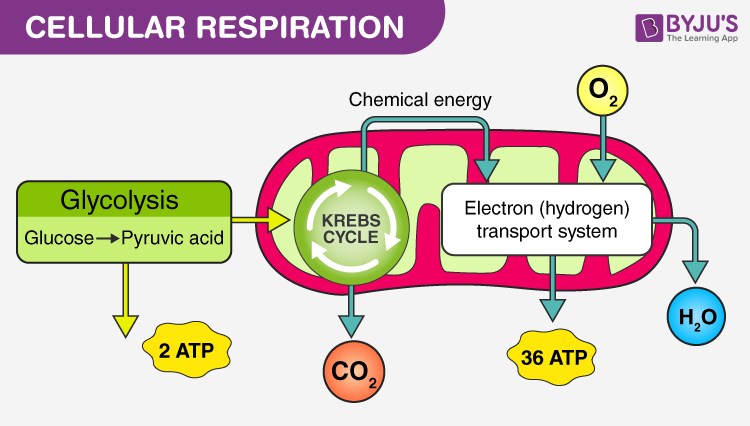
Cellular Respiration Respiration Anabolism And Catabolism
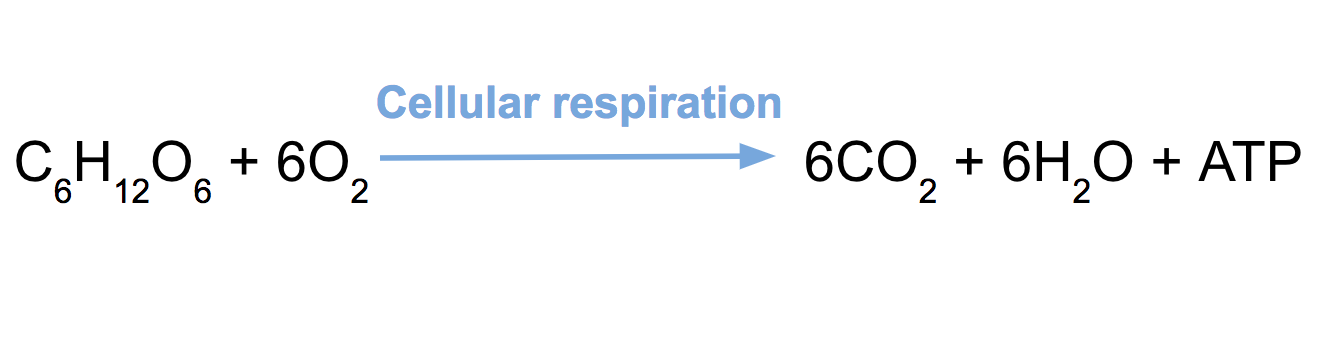
Cellular Respiration Review Article Khan Academy

Aerobic Respiration Bioninja

Cellular Respiration In Detail Youtube

Anaerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
11 Differences Between Aerobic And Anaerobic Respiration
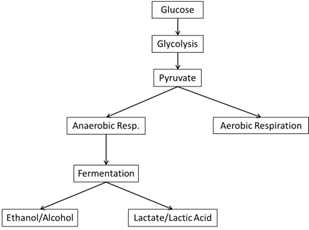
Cell Respiration Wyzant Resources

What Are The Inputs And Outputs Of Cellular Respiration Study Com

Anaerobic Respiration Bioninja
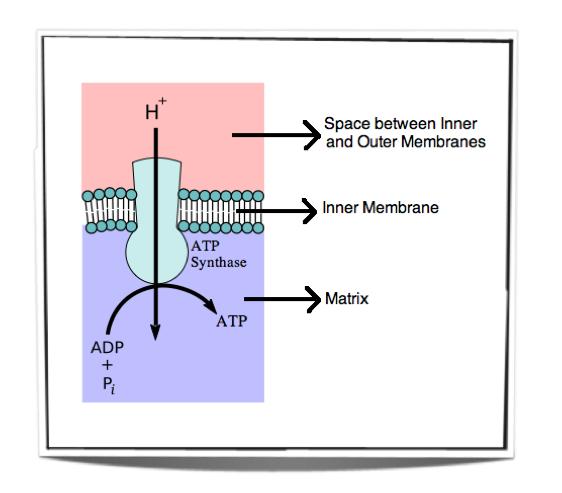
Ib Biology Notes 8 1 Cell Respiration

8 1 Cell Respiration Bioninja

Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy

7 1 Cellular Respiration A Biology

What Is Chemiosmosis Definition Process Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
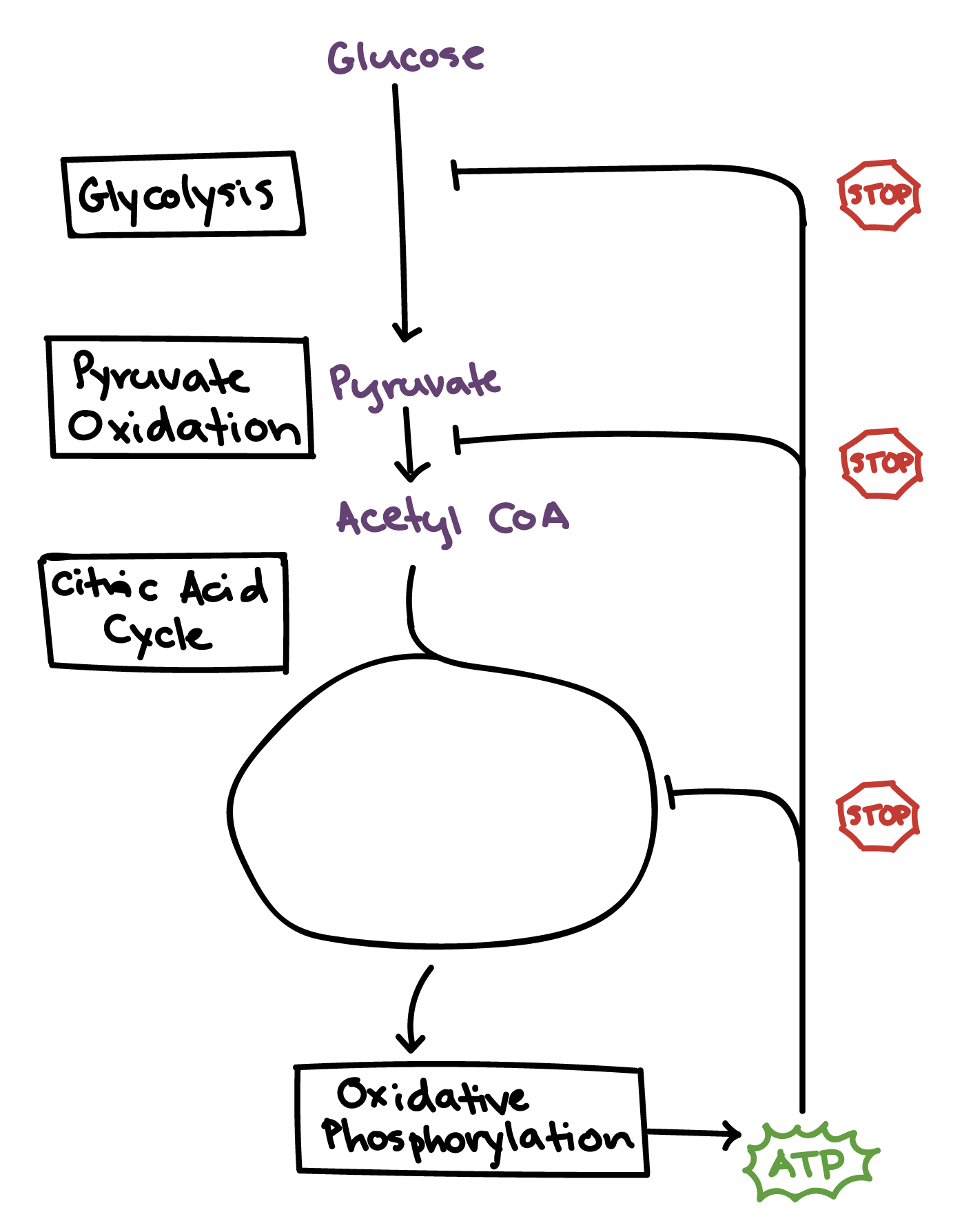
Regulation Of Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy

Aerobic Respiration Is A Biological Process That Takes Energy From Gl Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Biology Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration

Cellular Respiration Diagram Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Biology Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration

Cellular Respiration Guided Notes And Diagrams Printable Handout Cellular Respiration Biology Notes Biology Classroom
That's all about Cellular respiration meaning in biology, How to get a covid antibody test. The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells. Cellular respiration is the procedure by which cells obtain their energy in the shape of atp. Cellular respiration definition cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. The first step of cellular respiration glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm as the enzymes required for glycolysis are present in the cytoplasm. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form.

